What are bilberries good for?
Cranberries, also known as bilberries, are small, dark-blue berries with a sweet, slightly tart flavor. These delicious berries do more than just brighten up your favorite dishes: they also have remarkable medicinal virtues. Rich in antioxidants, vitamin C, fiber and essential minerals, these berries are invaluable for boosting your overall health. Their anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties contribute to the prevention and treatment of many common ailments, making them an ideal choice for those seeking a natural remedy.
Cranberries are known for their beneficial effect on the urinary system. In fact, thanks to their specific phytochemical compounds, they help fight urinary tract infections by preventing bacteria from clinging to the bladder walls. What's more, their natural diuretic action promotes the elimination of toxins from the body, helping to purify the urinary system. By regularly consuming these berries, you can maintain a healthy urinary system and prevent recurrent infections.
The anti-inflammatory properties of cranberries are particularly useful for relieving pain associated with conditions such as arthritis or gout. They work by reducing joint inflammation and soothing muscle pain. What's more, these berries are also known for their digestive benefits. Their high fiber content helps regulate intestinal transit, making them an excellent remedy for constipation. For those suffering from abdominal pain or digestive disorders, consuming lingonberries can offer natural and effective relief.
Did you know that cranberries can also improve your night vision? Thanks to their high anthocyanoside content, these berries strengthen retinal capillaries and improve microcirculation in the eyes. This can be particularly beneficial for people suffering from eyestrain or other visual disorders. What's more, research shows that these berries can play a role in preserving memory and cognitive health. The powerful antioxidants in cranberries help protect brain cells from oxidative stress, promoting better cognitive function and reducing the risk of age-related decline.
Cranberries contain a high concentration of antioxidants, particularly flavonoids, which help protect the cardiovascular system. These compounds help prevent the oxidation of LDL cholesterol, a key factor in the development of heart disease. In addition, they promote good blood circulation by maintaining the elasticity of blood vessels. Incorporating these berries into your diet can therefore significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease, while providing support for your overall heart health.
If you're looking for a slimming food, lingonberries are a perfect choice. Low in sugar and calories, they are ideal for those wishing to control their weight. Their high fiber content provides a natural appetite-suppressant effect, helping to reduce cravings and maintain a healthy weight. What's more, their ability to regulate metabolism and promote fat elimination makes them a valuable asset for anyone seeking to lose weight.
Iphym also offers dried Goji berries at the best prices in our online pharmacy.
How to use this plant
To get the most out of bilberry berries, it's important to follow the appropriate instructions. Here's how to prepare and consume these berries optimally:
To prepare a decoction, use 30-60 g of dried berries. Place in 1 liter of cold water, bring to the boil, then simmer gently for 10 minutes. Strain the mixture while it's still hot. You can leave it to cool and store it in the fridge. Drink the liter of decoction throughout the day, in small cups. For persistent diarrhoea, consult a doctor if symptoms last more than 3-4 days.
For eye and circulation disorders, take 55 g to 115 g of fresh fruit three times a day. For inflammation of the mucous membranes of the mouth and throat, make a decoction using 100 g of dried fruit in 1 liter of cold water, bring to the boil, simmer for 10 minutes, then use as a gargle.
Give your opinion on the advice for use and dosage of this product with our partner Verified opinions after your purchase.
Precautions for use
Prolonged use of cranberry leaves is not recommended due to the risks associated with chronic consumption: cachexia, anemia, jaundice and tonus disorders have been observed in animals with high doses (1.5 g/kg/day). On the other hand, moderate consumption of berries is harmless. Avoid consuming large quantities of fresh berries, as their laxative effect may cause intestinal discomfort.
What is it made of?
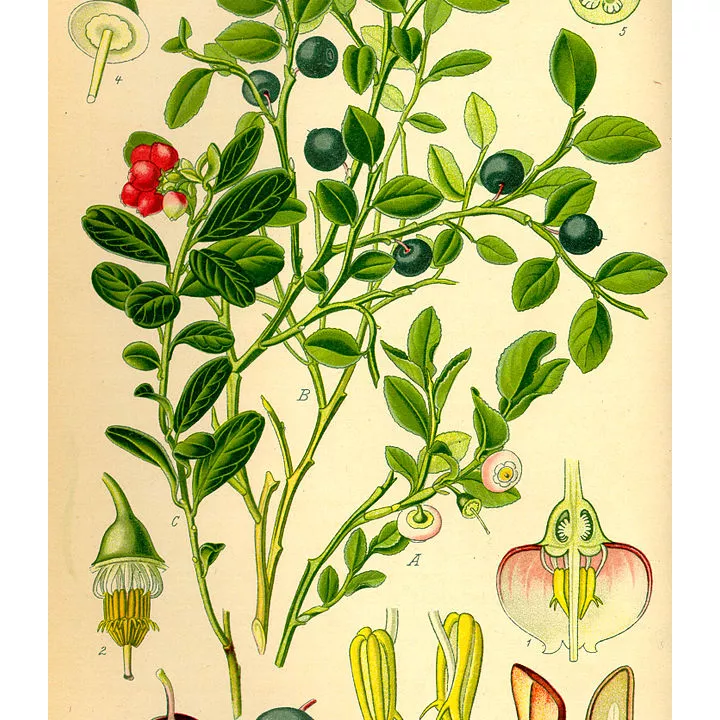
Latin name: Vaccinium myrtillus L.
Family: Ericaceae
Common names : Cranberry, lingonberry, bluet, brimbelle, wood grape, heather grape, aires
Parts used: Fruit
Origin: Northern and Central Europe, abundant in sparse woods with siliceous subsoil; in France, the plant is common in mountains up to 400 and 2500 m in altitude.
Presentation
Available in 100 g, 250 g or 1 kg formats.